- Safety Knights Monday Mailer
- Posts
- Newsletter 32nd Edition
Newsletter 32nd Edition
Good morning! Happy Memorial Day, we hope you’ve been able to enjoy time with family, friends and remember those you gave the ultimate sacrifice for us.
THIS WEEK’S TIPS
This week’s safety upgrades:
PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT
This Weeks Professional Development Tip
New OSHA HazCon Rule
State Rule Changes
10 Key Actions to Establish Your Mental Health Program
OSHA UPDATE
HazCom Changes You Need to Know?

OSHA's recent update to the Hazard Communication (HazCom) Standard brings it in line with the latest version of the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), Revision 7, published in 2017. This alignment aims to enhance the consistency and effectiveness of chemical hazard communication across borders, particularly with major trading partners like Canada and the European Union.
The revisions address feedback and issues raised since the previous update in 2012, including clarifications on label requirements for small containers and guidance for very small containers. These adjustments aim to make compliance more practical for businesses while maintaining worker safety standards.
One notable change is the requirement for chemical manufacturers and importers to consider downstream uses and foreseeable emergencies when classifying hazards. This ensures that potential risks associated with the use and handling of chemicals in various workplace scenarios are appropriately communicated.
Additionally, the update harmonizes SDS requirements with GHS guidelines and Canadian regulations, allowing for greater consistency in hazard communication documentation. This facilitates the exchange of chemical information between countries and simplifies compliance for businesses operating internationally.
Overview of the Changes to the standard include:
Revised criteria for classification of certain health and physical hazards
Revised provisions for updating labels
New labeling provisions for small containers
New provisions related to trade secrets and technical amendments related to the contents of safety data sheets
Related revisions to definitions of terms used in the standard
Shout out to Drew Hinton for bring this info to the Safety Knights Community.
TECHNOLOGY NEWS
The Matrix for Workplace Safety.

Dr. Diana Rodriguez Coca and Dr. Leslie Stockel from Oklahoma State University are undertaking a two-year research project funded by The MEMIC Group to develop virtual reality (VR) training materials for workplace safety. The project, titled "Virtual Reality Study of Line of Fire Incidents," aims to increase awareness among manufacturing and construction workers about the dangers of being struck by or caught in-between equipment due to their physical placement.
The research will involve creating VR scenarios based on real-life incidents resulting in workplace fatalities. These scenarios will be developed by Tanvir Rahman Rifat, an MS student in engineering technology specializing in fire safety and explosion protection. The study will proceed in two phases: first with untrained participants and then with the same participants after they receive training using the developed materials.
Participants will be immersed in VR simulations to identify hazards and risks related to "line of fire" situations, with the goal of raising awareness to prevent serious or fatal injuries. The project aims to address a significant issue, as statistics show that a considerable percentage of workplace fatalities and injuries are related to contact between workers and materials or equipment.
The study will take place in the VR studio of the Fire Protection and Safety Engineering program at Oklahoma State University. Using VR simulations ensures participant safety while offering cost savings and increased efficiency in training. Previous research has shown promising results for VR-based education compared to traditional methods.
The outcomes of this research will contribute to expanding knowledge in the field of workplace safety and inform the development of future training materials aimed at reducing the short- and long-term impacts on workplace safety and employee health.
PRESENTED BY REDALERT WAX
No One Reads.

You ever feel like a complete fool after slipping on that wet floor? There are going to be some places you can’t do anything about that. But where you have a say, make the move to Red Alert Wax and regain your floor dignity.
As easy as 3 steps.

MENTAL HEALTH
10 Key Actions to Establish Your Mental Health Program.

A notable surge in lost time injuries, doubling the previous year's rate, served as the catalyst for Jennifer Richardson, the Director of Environment, Safety, Employee Health, and Wellbeing at the Royal Canadian Mint, to embark on the mission of establishing a comprehensive mental health program. Despite lacking a background in mental health, Richardson spearheaded this initiative, driven by the imperative to address escalating injury rates and diminishing employee engagement. Here’s a breakdown of 10 Key Actions outlined in her journey:
1. Identify the Need: Recognize any trends or issues within the organization that indicate a need for a mental health program. This could include rising lost time injury rates, lower employee engagement, or reported mental health challenges.
2. Gain Leadership Support: Present the need for a mental health program to the organization's leadership or board. Highlight the potential benefits and urgency of addressing mental health concerns in the workplace.
3. Develop a Strategy: Create a comprehensive strategy for the mental health program, outlining goals, objectives, and key initiatives. Consider starting with simple, impactful actions that can be implemented quickly.
4. Establish a Working Group: Form a Mental Health Working Group (MHWG) composed of employees with lived experience or interest in mental health. This group can provide valuable input and help drive the program forward.
5. Implement Training and Awareness Programs: Roll out mandatory training sessions, such as Mental Health First Aid training for leaders and employees. Launch awareness campaigns, such as the 'Not Myself Today' campaign, to promote mental health awareness and reduce stigma.
6. Leverage Creativity and Collaboration: Be creative in implementing resources and initiatives, especially considering the diverse workforce and accessibility to resources. Collaborate with various departments, including HR, to ensure a holistic approach to mental health support.
7. Measure Success and Adapt: Monitor the effectiveness of the program through surveys, feedback, and key performance indicators. Adapt the program based on feedback and evolving needs within the organization.
8. Integrate into Organizational Culture: Aim for the mental health program to become ingrained in the organization's culture, transcending its initial objectives. Encourage leadership support and participation to foster a culture of openness and support around mental health.
9. Drive Continuous Improvement: Continuously strive to improve and expand the mental health program. Stay updated on best practices, industry trends, and new resources to enhance the support provided to employees.
10. Share Success Stories and Learnings: Share success stories and learnings from the mental health program with stakeholders within the organization and beyond. Consider speaking at industry events or conferences to inspire others and drive positive change in workplace mental health.
WORKER SAFETY
Climate Change and Worker Safety.
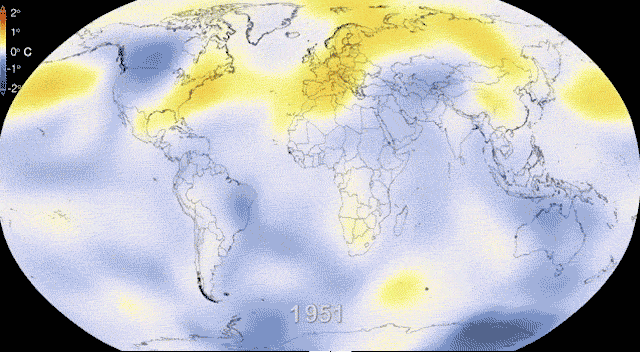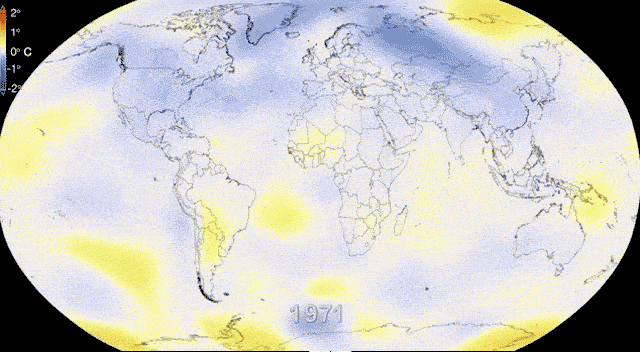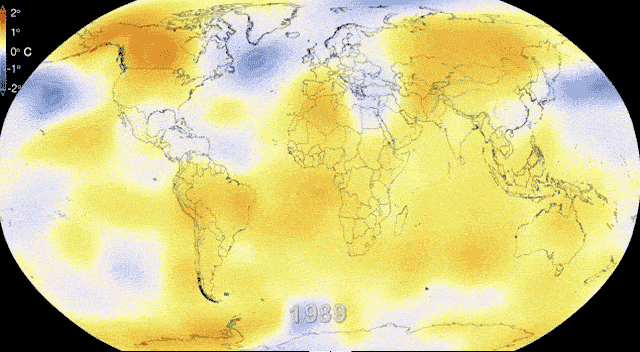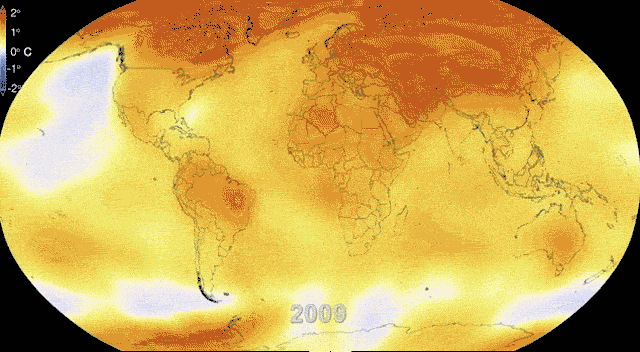
Climate change presents a multifaceted challenge to worker health and safety, with its effects permeating various industries and necessitating tailored adaptation strategies. Here's a deeper look at some key aspects:
Impact on Worker Health: Climate change contributes to rising temperatures and more frequent extreme weather events, leading to a range of health issues for workers. Heat-related illnesses, such as heat stroke and exhaustion, become more prevalent, especially among outdoor workers who bear the brunt of intense heat and sun exposure. Additionally, increased air pollution, both indoors and outdoors, exacerbates respiratory problems and can lead to other ailments like skin conditions and cardiovascular diseases. Mental health concerns, including eco-anxiety stemming from the worsening climate, are also on the rise among workers facing these environmental stressors.
Vulnerable Sectors: Certain sectors face heightened risks due to climate change. Outdoor workers, including those in construction, forestry, and urban infrastructure maintenance, are particularly exposed to environmental hazards like UV radiation, air pollution, and extreme heat. Agriculture and fisheries also grapple with the unpredictable impacts of climate change on crop yields, soil health, and oceanic conditions. Furthermore, healthcare workers face increased challenges in dealing with infectious diseases, aggravated by indoor air and water pollution.
Regulatory Response: Regulatory bodies like OSHA and NIOSH play a crucial role in addressing climate-related workplace hazards. OSHA's Emergency Action Plan standard, for instance, mandates that employers have strategies in place to deal with severe weather events. NIOSH provides resources and guidelines to protect workers from extreme heat and wildfire smoke exposure. Additionally, organizations like the EPA and ILO offer models and agendas to promote safe working conditions amidst climate change.
Improvement Strategies: Employers can implement various strategies to safeguard workers' health and well-being in the face of climate change. These include providing restorative breaks, access to shaded and air-conditioned spaces, and training programs on stress management and self-care. Investing in robust personal protective equipment (PPE), such as cooling vests and masks, is essential for minimizing exposure to environmental hazards. Moreover, developing climate risk emergency response plans ensures that workers know how to react during crises effectively.
Technology and Innovation: Advancements in technology offer opportunities to enhance worker safety in a changing climate. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and patches, can monitor vital signs and provide real-time health data. Mobile apps facilitate self-reporting of health conditions and offer personalized health advice. Predictive analytics enable companies to schedule work based on weather forecasts, minimizing exposure to extreme conditions. Drones can surveil worksites, assessing environmental parameters like temperature and pollution levels.
By recognizing the intricate interplay between climate change and worker safety and implementing comprehensive measures to address these challenges, organizations can better protect their workforce and contribute to broader efforts to combat the climate crisis.
STATE CHANGES
NJ: Gym, Tan, Heat Protection?

New Jersey's Senate Labor Committee has recently pushed forward a bill, sponsored by Sen. Joe Cryan, aiming to establish a heat stress standard in the state by June 1, 2025. The proposed legislation, labeled S. 2422, compels employers to craft, implement, and uphold a comprehensive heat-related injury and illness prevention plan for their workers within 30 days of the bill's effective date. This plan is mandated to encompass various measures, including provision for paid rest breaks, access to cool drinking water, availability of shaded or climate-controlled areas for workers to cool down, protocols for emergency response in case of heat-related injuries, and strategies for acclimatizing workers to high-temperature conditions.
Under the bill's provisions, employers failing to comply with these requirements could face fines ranging from $500 to $5,000, coupled with potential jail time of 10 to 100 days. During a committee hearing on May 6, Gerardo Cortez, a UPS driver and shop steward for Teamsters Local 177, emphasized the importance of such legislation in safeguarding workers, drawing from his own experiences of working in extreme heat conditions.
However, opposition to the bill has been voiced by the New Jersey Farm Bureau, asserting that the state's farmers have long been managing heat stress through established practices. According to Ashley Kerr, a research associate for the farm bureau, these practices typically include adjusting work schedules, providing cool drinking water, offering additional rest breaks, and other similar measures.
The bill, S. 2422, has been referred to the Senate Budget and Appropriations Committee for further consideration. Additionally, a companion bill, A. 3521, was introduced in the General Assembly and is currently under review by the Assembly Labor Committee since February.
Cal/OSHA War on Silicosis
Cal/OSHA is ramping up efforts to address the rising cases of silicosis among stone workers in California. Man-made stone, commonly used in construction, contains high levels of crystalline silica, which can cause severe lung damage when inhaled. Since adopting an emergency temporary standard in December 2023, Cal/OSHA has intensified enforcement, shutting down stone cutting shops not meeting safety standards. A public meeting on May 16 will consider a revised proposal for readoption of the emergency temporary standard. A bilingual public awareness campaign provides resources on safety equipment and practices. Over 100 stone workers in California have developed silicosis since 2019, with at least 10 deaths among workers under 40. Cal/OSHA aims to reduce silicosis risks through advocacy, education, and enforcement. Director Katie Hagen emphasizes the importance of proper safety measures to protect workers from this fatal disease, stressing the need for water systems, dust cleaning, and respiratory protection.
DON’T FORGET YOU DISCOUNT
Don’t forget your discount SKsaves10
Compliance training online is the way to go because they've got the best content and customer service in the biz. With over 30K trusted clients, including government agencies and universities, their certificates are accepted on a federal level. Trust us, we've been in business since 2008.
NEWS
Your Virtual Water Cooler
🔊[Podcast] Going Beyond Compliance-Why just meeting the requirements might not be enough
“Looks Like An OSHA Violation But OK”: 50 Examples Of Ridiculous Work Safety (Best Of All Time)
Creating a Safe Workplace: A Guide for Self-Storage Operators in 2024
New institute launched to advance global leadership in safety
EV manufacturing: Protecting worker safety in the gigafactory boom
SHARE THE NEWS
Enjoying the newsletter? Share it and earn some free Safety Knight swag. The more referrals you have the more you earn!
All you need is one to start earning.




